What are Google search operators?
Google search operators are combinations of words and symbols that help improve search results. They are used for technical audits and much more.
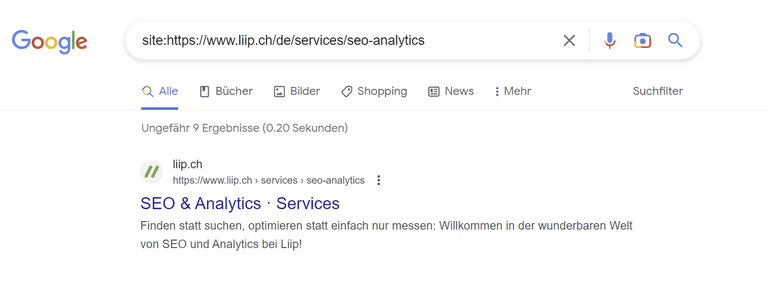
If you are in SEO, you are probably already familiar with the search operator “site:” There are tons of things that can be done with the “site:” search operator, typically, it’s used to find out if a page is indexed, which means see if a page is on Google.
Google search operators advantages
In my opinion, there are 3 main advantages to using Google search operators:
-
They are free to use, and SEO tools are often expensive.
-
It allows you to better understand how Google perceives/indexes your site and that of your competitors (we will get back to this later in the blog post).
-
They are easy to use. If you know how to use Google, you know how to use search operators.
How to use Google search operators?
1. Exact match
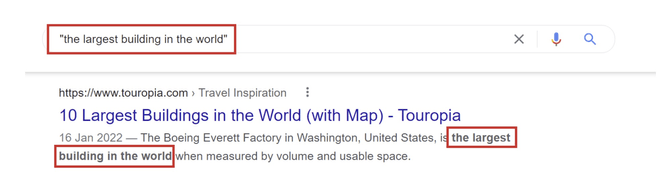
Quotes allow you to get an exact match of a word or phrase. In this case, we have…
2. Combine searches
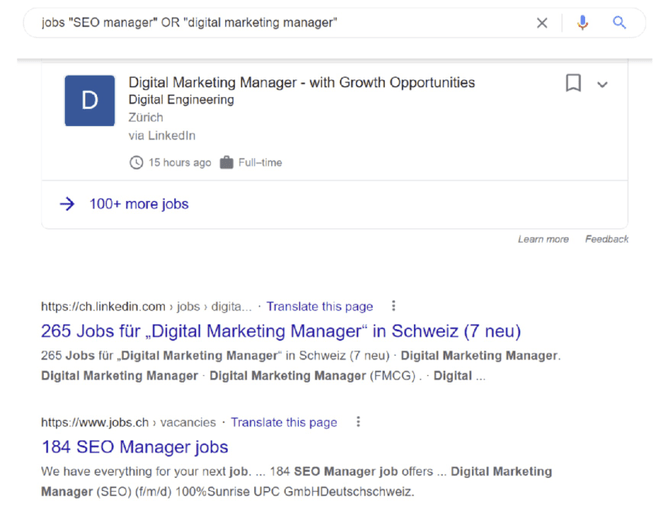
The search operator OR, alternatively you can also use the vertical bar (|), allows you to combine terms.
In this example, we search for jobs containing the keyword "SEO manager" or "digital marketing manager"
3. Exclude a domain from the search
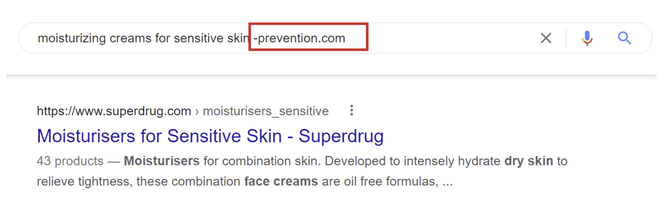
Let’s say, we are entering the UK market, and we know that prevention.com is the leading e-commerce shop for moisturising creams for sensitive skin. As we are aware of their role, we can exclude it from the SERP, as in the example below, resulting with a list of competitors except for prevention.com
4. Exclude a word from the search
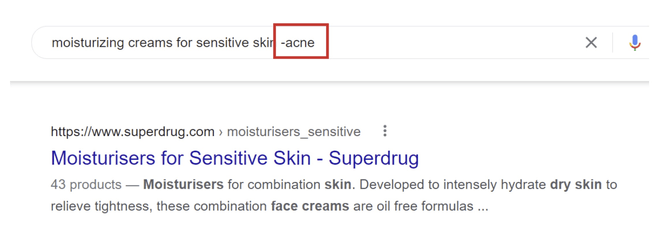
Suppose our target group for moisturising creams are women between 30-40y; the chances are they don't have acne problems. If we search for sensitive skin moisturisers while excluding the problem of acne, we can use “-acne”.
5. Expand a search
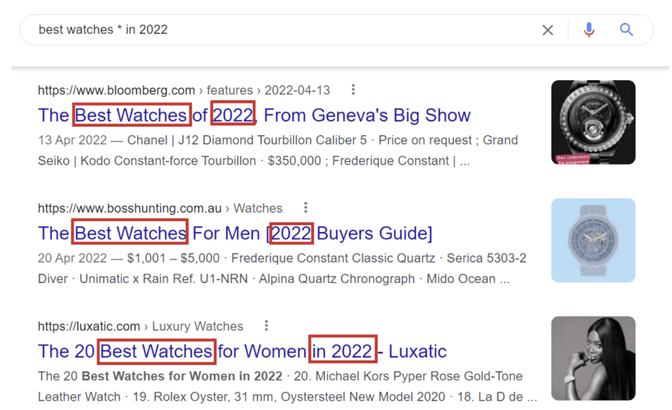
An asterisk (*) can act as a wildcard. Google treats the asterisk as a placeholder for one or more words. In the below example, we have Best watches for Men in 2022, Best watches for Women in 2022
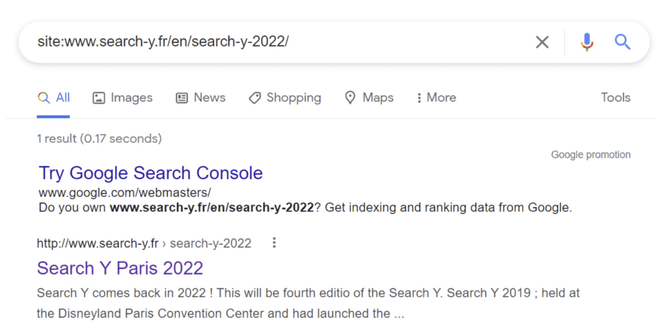
6. Search from a specific domain, URL or URL prefix
As mentioned at the beginning, this is the “site:” search operator. It can be used to find out if a page is indexed and much more.
7. Find information before/after a date
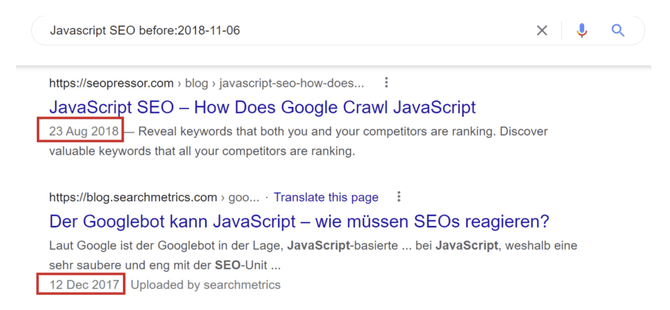
Suppose you wish to know how JavascripSEO was positioned before November 6th 2018. Using the search operator “before:2018-11-06” we have a list of blog posts written before that date. The same happens with the search operator “after:2018-11-06”
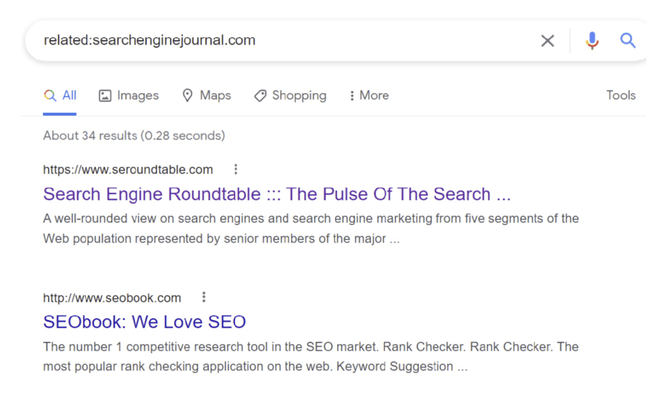
8. Find similar sites
Using "related" allows you to find similar sites. Be aware this doesn't always work, but when it does, it's great because it will give you insight into which website Google considers similar to yours, which implies that, ultimately, they are your direct competitors.
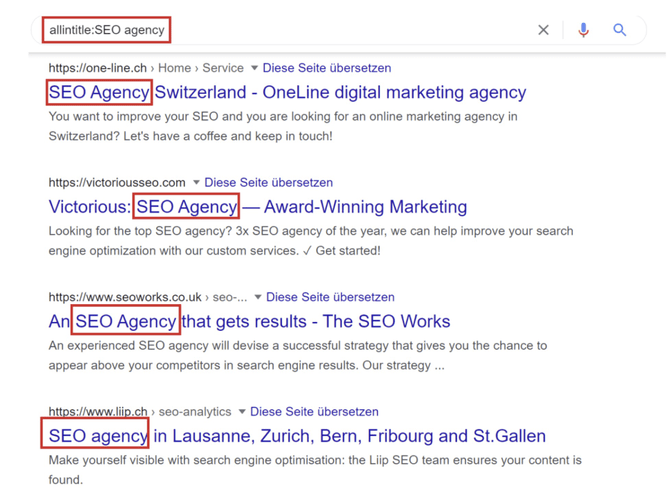
9. Find a title with keywords
Allintitle: Returns pages containing all the words used in the title search.
Example of allintitle: SEO Agency is the search word.
Intitle: Works the same as allintitle, except it only searches for the word directly following the command.
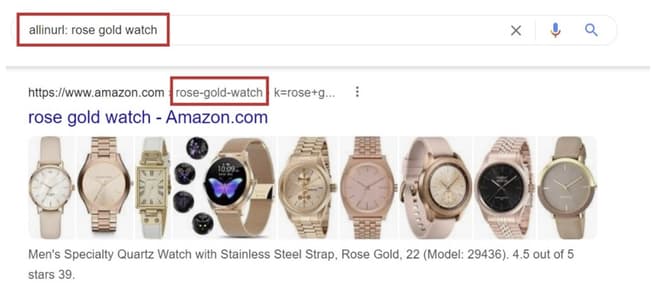
10. Find a keyword in the URL
Allinurl: Links to pages that contain all of the words used in the URL
Inurl: Refers to pages inurl:rose, inurl:gold, inurl:watch
How to combine them?
Now that we know some of the most essential search operators, let’s combine them to obtain some valuable information.
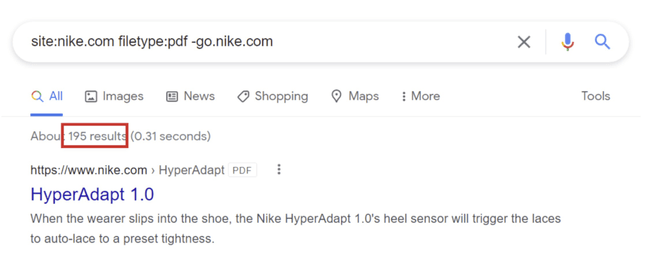
1. How to find PDFs and other documents
With the filetype operator, it is possible to find out if a site has documents that should not be indexed, for example…
2. What's the next featured snippet?
4 years ago, I did a course with Barry Adams, and he told us about a trick to know which feature snippet follows the one you see.
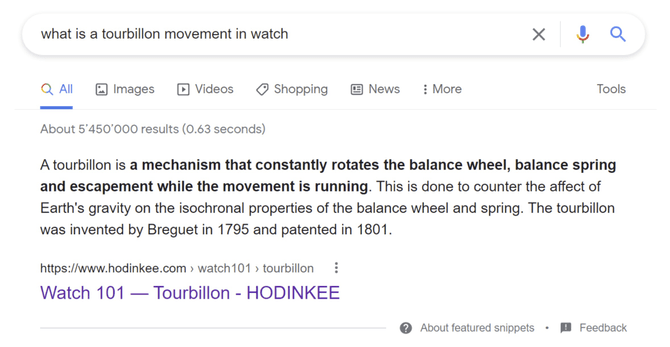
The question "what is a tourbillon movement in watch" generates a featured snippet, as shown in the first image.
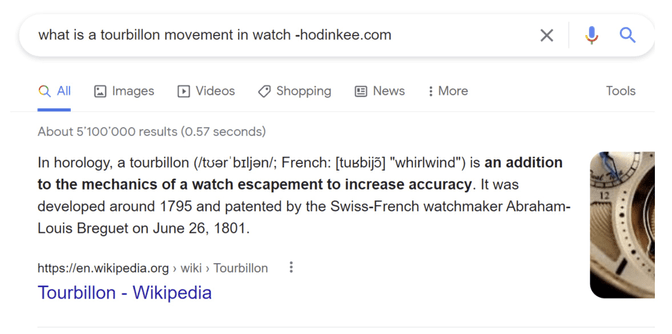
By using "-" we can find the next feature snippet that Google would propose.
Imagine that you are in SEO, and you see that one of your competitors has the featured snippet...
Using the "-" domain, as in the example, you will discover that the next company with the featured snippet is the one you are working for. That, for sure, gives hope. You know that with some more effort, you can obtain the featured snippet.
3. Find internal linking opportunities
Imagine, you just wrote a new blog post and wish to create better internal linking. Internal linking has many benefits, but probably one of the most useful for a new blog post is to facilitate crawlers' discovery of the last blog piece you wrote.
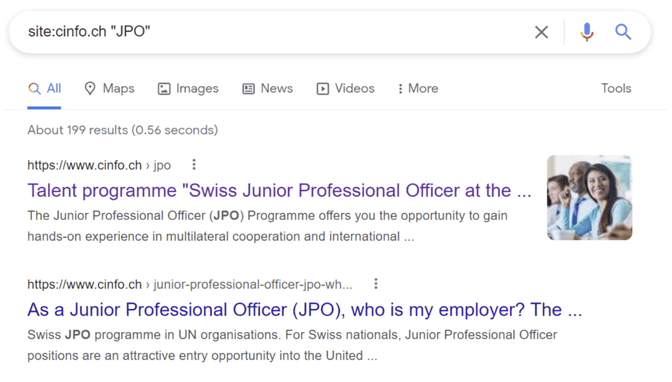
In this example, we take a website called Cinfo, one of their missions is to find suitable people that work for the UN, and one of their job titles is JPO. Let’s assume that we just wrote a blog post about JPO jobs and want to find internal linking opportunities. You would then use “site: + “keyword”
4. Find insecure pages
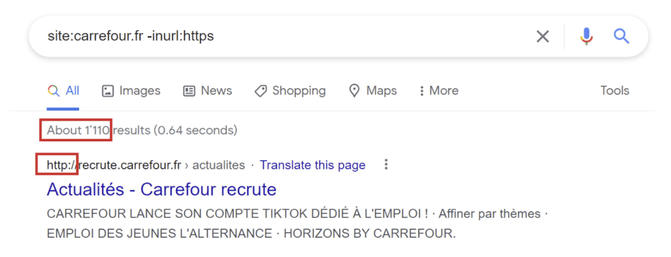
Let’s say you work for Carrefour, and we are doing an audit. You can instantly find out if you have insecure pages by using “site: -inurl:https”.
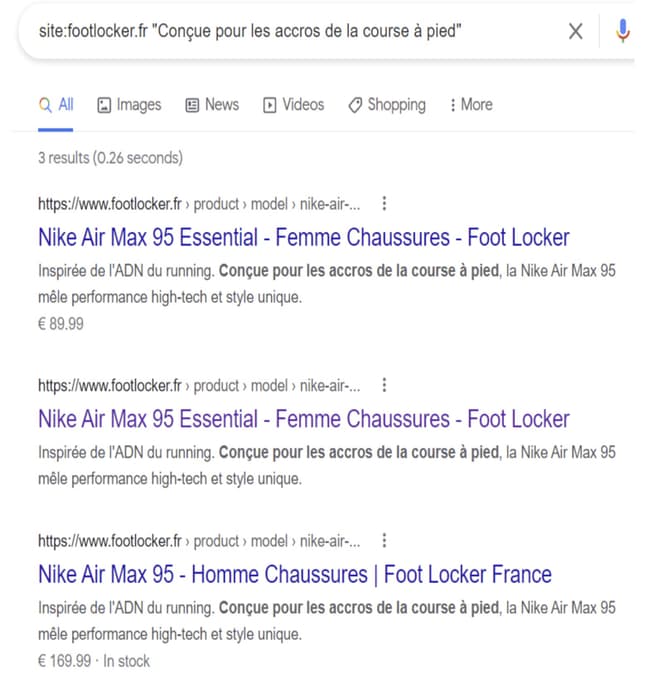
5. Duplicate content within a site
Internal duplicate content is when your website has multiple URLs for the same content. As shown here:
Conclusion
Google search operators give you tons of information. Above, you have some of the most common examples. However, suppose you have an SEO question related to a website. In that case, there are great chances that by combining the search operators, you can get the answer you are looking for, especially if it’s related to indexing. If you realize Google isn't indexing your pages the way you want. Don't hesitate to contact one of our SEO specialists, it's part of our job to find indexing problems and fix them.